Computer Basics – Absolute Beginner Guide
This page is designed for someone who has never learned computers before.
1️⃣ What is a Computer?
A computer is an electronic machine that takes input, processes it, and gives output.
You give input using a keyboard, mouse, or touchscreen.
The computer processes data using its internal parts.
Finally, it shows results on the screen or speakers.
Examples: Laptop, desktop, tablet, smartphone.

2️⃣ Hardware
Hardware means the physical parts of a computer.
These are the parts you can see and touch.
Common hardware includes keyboard, mouse, monitor, CPU.
Without hardware, a computer cannot exist.
If hardware is damaged, it usually needs repair or replacement.

3️⃣ Software
Software is a set of instructions that tells hardware what to do.
Software cannot be touched, but it can be seen on the screen.
Examples include Windows, Chrome, WhatsApp, MS Word.
Every task on a computer needs software.
Without software, hardware is useless.

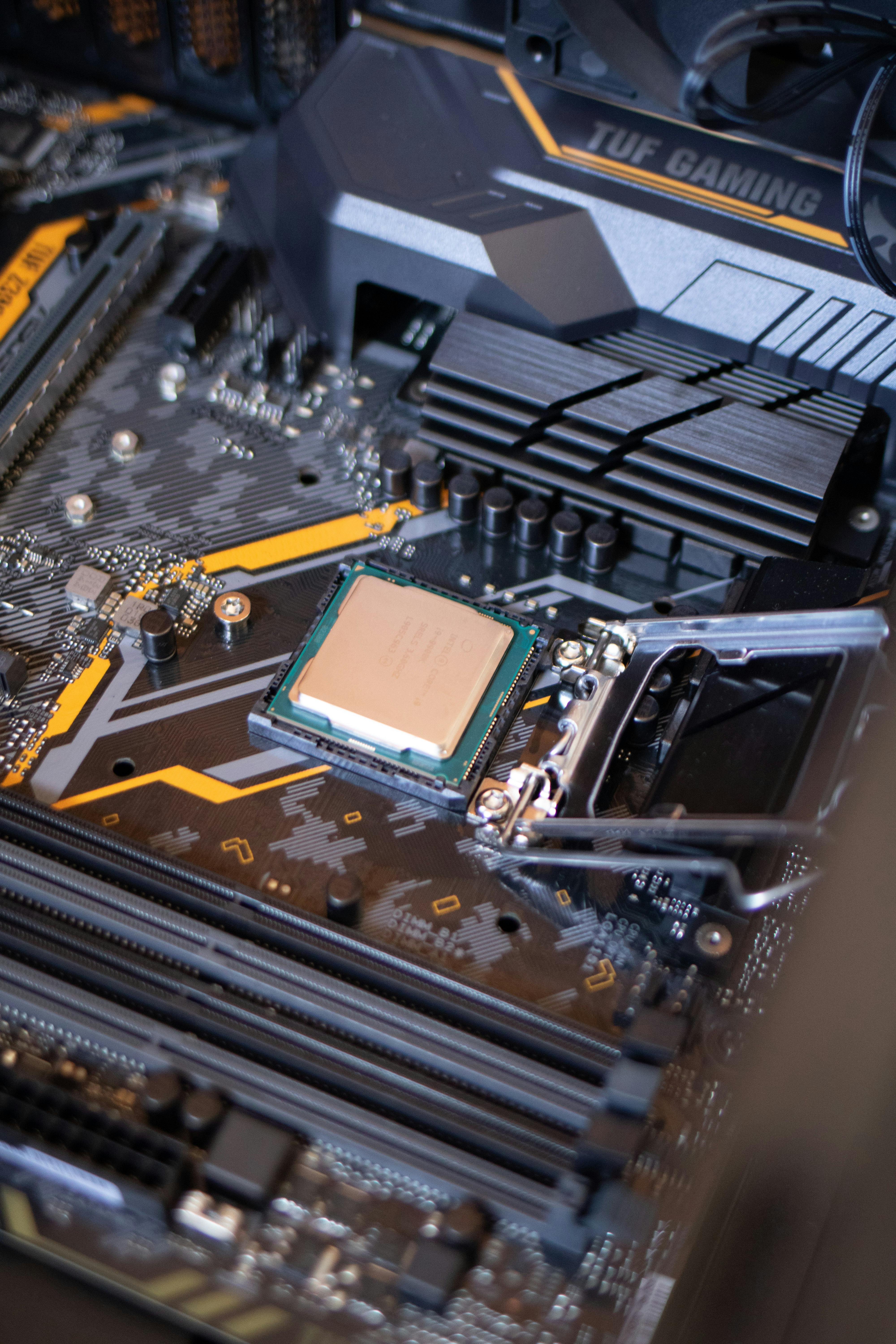
4️⃣ CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The CPU is called the brain of the computer.
It processes instructions and performs calculations.
Every action you perform goes through the CPU.
A faster CPU means programs run quicker.
The CPU is located inside the system unit.

5️⃣ Internet Basics
The Internet is a global network that connects computers.
It allows people to share information worldwide.
You can use the internet for emails, videos, learning, and shopping.
Websites are opened using browsers like Chrome or Edge.
The Internet has become an important part of daily life.

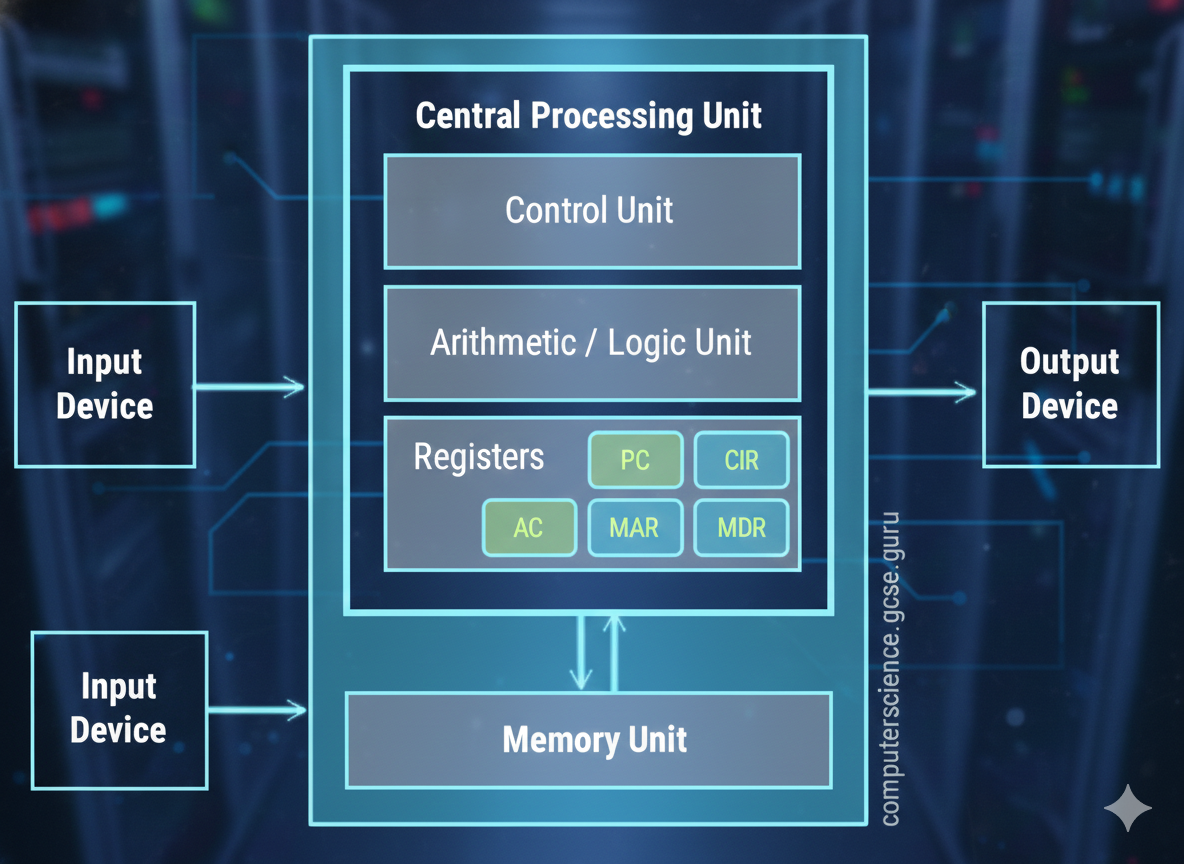
6️⃣ The CPU & F-D-E Cycle
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is known as the brain of the computer.
It processes instructions and controls all operations.
Main CPU Components:
- ALU: Performs calculations and logical operations
- Control Unit (CU): Directs data flow inside the CPU
- Registers: Very small, very fast memory
Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle:
Fetch → instruction is taken from memory
Decode → instruction is understood
Execute → instruction is performed
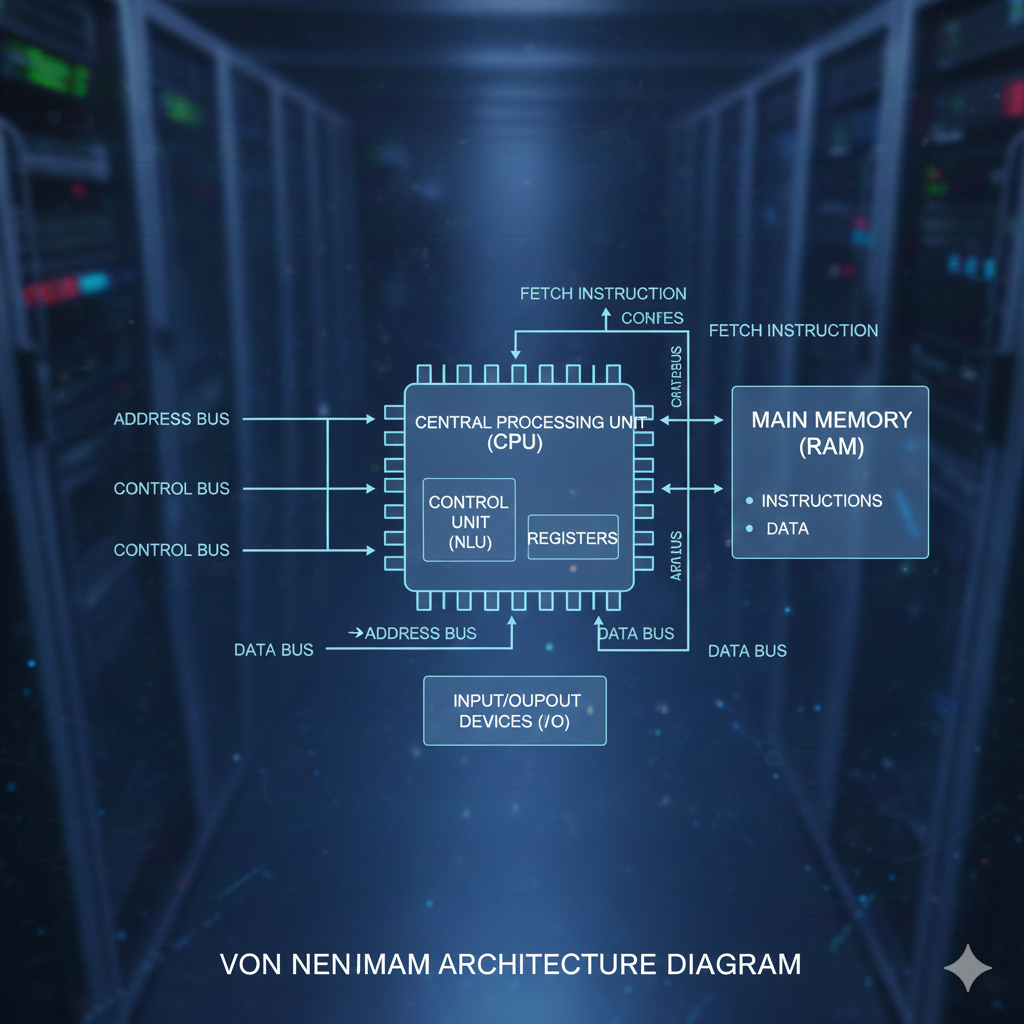
7️⃣ Von Neumann Architecture
This is a standard computer design model.
It stores instructions and data in the same memory.
The CPU fetches both from one shared location.
This design makes computers simple and efficient.
Most modern computers still use this concept.
8️⃣ CPU Performance
CPU performance determines how fast a computer works.
Key factors:
- Clock Speed: Higher speed = more instructions per second
- Cache Size: Fast memory that reduces delays
- Number of Cores: Allows multitasking
Modern CPUs use multiple cores for better performance.

9️⃣ Storage & Memory
Computers use different types of storage.
Primary Storage:
Fast memory directly accessed by the CPU (RAM).
Secondary Storage:
Long-term storage like SSDs and HDDs.
Secondary storage keeps data even when power is off.

🔟 Embedded Systems & System Software
Embedded Systems are computers built into devices.
Examples include washing machines, cars, microwaves.
System Software controls hardware.
Examples include Operating Systems and utilities.
Without system software, applications cannot run.

🧠 Quiz: Test Your Knowledge
1. What is a computer?
2. Which one is hardware?
3. Which one is software?
4. Which part is called the brain of the computer?
5. Which device is used to see output?
6. Which memory is temporary?
7. Which stores data permanently?
8. Internet is mainly used for?
9. Which is NOT hardware?
10. Without software, a computer is?
🧠 Advanced Concepts
1. What does the ALU do?
2. What is the first step of the F-D-E cycle?
3. What does Von Neumann architecture store together?
4. Which storage is non-volatile?
5. Embedded systems are found in?